The most frequent causes of tooth damage are due to already broken teeth by any accident and infections or plaques. Cavities are the major cause of tooth decay that causes holes in the enamel, which is the hard outer covering of the tooth. Root canal is particularly done to save the badly damaged tooth due to infection, as a replacement for extraction. A root canal is done by a root canal specialist or endodontist and the procedure is known as endodontic treatment. It is needed if the middle part of the pulp inside the tooth that consists of all the blood vessels and nerves is infected and causes inflammation. Together, all these factors contribute to tooth damage that can lead to pulp decay, and inflammation then affects the nerves supplying blood, causing severe pain.
The Signs That a Root Canal Is Needed are:
- Stabbing pain while chewing or biting
- Sensitivity on eating hot or cold
- Pimples on gums
- Cracked teeth with inflammation
- Swollen and painful gums
- Deep tooth decay with damaged gums
Table of Contents
Feel free to skip ahead if one topic catches your eye:
- What are Cavities?
- When does a dentist suggest Root canal treatment?
- When does a dentist suggest Extraction and Implant?
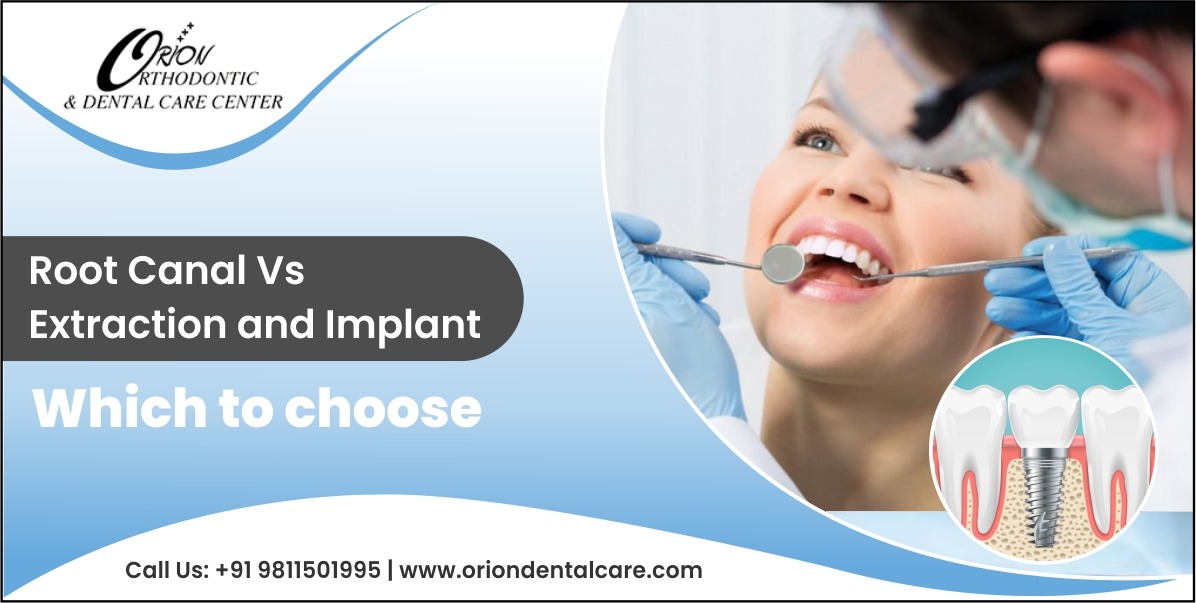
1. Root canal VS extraction and implants:
An infection in the pulp of the tooth causes the nerve inside to get irritated and cause severe pain. The extraction of the same tooth and the infected tissue, and the nerve helps relieve the pain. Risks of extraction are more severe than with root canal therapy.
The risks of tooth extraction are:
- Loss of bone mass and volume on which the extracted tooth laid.
- Nearby teeth might position out of place with time, causing misalignment of the teeth.
- Creating a vacant space in the jaw causing lodging of food, leading to cavity formation.
- Risk of loss of neighboring teeth is increased.
Root canal treatment is a conservative and non-painful procedure, unlike the misconceptions. This procedure helps clean out all the damaged tissue and nerve from inside the tooth. A special material known as gutta-percha is used to fill inside the outer covering of the tooth. No medical procedure can be completely risk-free and hence root canal procedure also has its own risks, which are:
- Complete removal of the infection from inside the tooth is not possible at times which may need endodontic treatment.
- A crown good in quality is needed to cover the root canal-treated tooth, as the root canal procedure weakens the tooth and makes it susceptible to fractures.
- A good quality crown and root canal procedure can be expensive at times.
- Few research says that root canal treatment can cause systemic illness due to the nerve affected, but this theory is not complete and does not have enough evidence yet.
- The tooth may be too damaged for the procedure, and the dentist may know that the damage is too severe, and the tooth cannot be saved after the whole procedure is done.
- Severe complications like abscess formation can lead to tooth extraction.
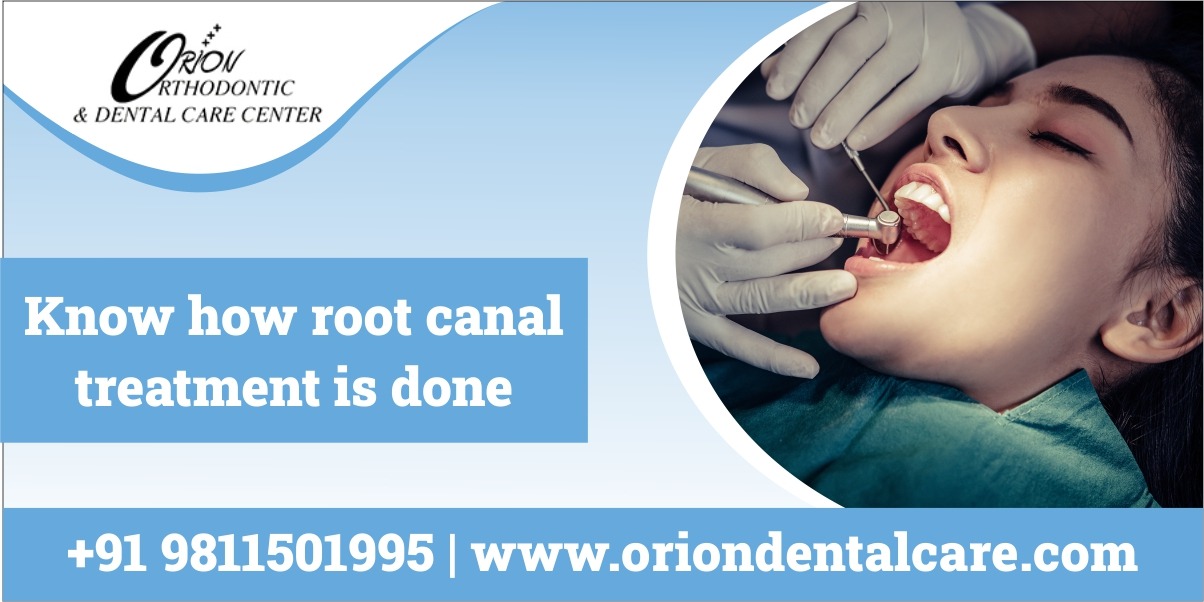
- Procedure of Root Canal Treatment
Firstly, an X-ray of the tooth is done to determine the pulp chamber, and then a local anesthetic is administered to avoid pain to the patient. A rubber sheet is placed to avoid and saliva from the surrounding. Then the crown is drilled to expose the pulp chamber and remove all the diseased and infected pulp from inside the tooth, the created space is disinfected and filled with gutta-percha and then covered with dental cement to seal the tooth. The seal is then shaped by an irrigation method, after which the tooth is covered with a crown and is cemented in place to avoid displacement and provide longevity to the tooth. Root canal procedure is successful with a rate of 95%, and the treated tooth can usually last for a lifetime.

2. When does a dentist suggest Root canal treatment?
Inflammation in the tooth or abscess beneath can progress into a major infection and lead to complete loss of function if not treated timely. Hence root canal procedure came into action to retain the function and outer appearance of the tooth. It also prevents the neighboring tooth from damage and excessive strain, as in the case of tooth extraction.
The techniques have advanced now that the patient no longer experiences major pain due to the use of local anesthetic as they numb the nearby area. The use of an anesthetic helps ease the pain caused by inflammation and helps carry out the procedure with relative ease.
Post-treatment guidelines after a root canal procedure include:
- Eating anything just after the procedure is not advisable as the area is numb and may lead to accidental nipping of the tongue. It is advised to stay on fluids until the numbness goes away.
- Consumption of antibiotics as directed by the doctor.
- Maintenance of oral hygiene with frequent cleaning and teeth flossing is essential after root canal treatment.
- Hard and crunchy stuff is advised not to be consumed few days as it can lead to displacement or damage to the crown.
- The temporary filling on the teeth needs to be weared off for the crown to be placed perfectly, but if the filling wears off completely, it needs to be done again to place the crown.
- Until the procedure is complete with a permanent filling or crown, it is advised to avoid chewing with the tooth and prevent the fragile tooth from breaking before it can be fully restored.
- It generally takes a week to recover from the procedure entirely.
3. When does a dentist suggest Extraction and Implant?
Because of the following reasons, extraction maybe advised by the dentist:
- Severe Damage or Tooth Decay– When the bacteria spread into the soft tissue of the tooth, to the dental pulp. The pulp consists of connective tissue and blood vessels and causes severe pain, inflammation, and infection. If the root canal infection is left unaddressed at this stage, it leads to abscess formation. Abscess formation can cause excruciating pain, and the infection can reach the ear, jawbone, or even brain under extreme conditions, requiring tooth extraction.
- Gum Disease – This disease is caused by infection of the gums and may lead to tooth extraction as it reaches roots and the alveolar bone. The most common cause is bacterial built-up or plaque that leads to tooth infection and later extraction if left untreated.
- Affected Wisdom Tooth – If a wisdom tooth is affected or blocked from coming out. To prevent the risk of an infection that may lead to gum disease for such teeth extraction is recommended.
- Teeth Overcrowding- It is a common problem in females as their jaws are smaller than males. Overcrowding causes difficulty in eating, even in speech, due to lack of space. Hence extraction is needed to realign the teeth.
- Accident or Injury- If the tooth has undergone damage due to an accident or injury, the dentist would advise extraction as preserving the teeth would be very expensive and time-consuming.
Dental implants are the top option for tooth backup due to the following reasons:
- These dental implants are made to last for a lifetime and do not need any changes.
- They have a success rate of 95%, showing how successfully these implants can bond to the patient’s jawbone.
- Implants imitate a natural tooth.
- Implants also protect from the shrinking of the jawbone after tooth extraction.
- It also provides a perfect base for the placement of the crown.
- One can consume anything according to their will without the risk of moving, sliding, or breaking.
Takeaway
Therefore it is advisable to contact a Dentist when suffering from tooth or gum ache and get a checkup done at first. This will help to address the root cause of the issue at first and avoid any further complications. At Orion, you’ll get the best suggestion and treatment as per your concern.
FAQ
- Root canal vs. Implant
If the tooth has major decay and you’re ready for a high cost treatment then one may go for an implant for the long term. But if the person prefers to keep their own tooth with the risks, a root canal can be cost effective and less invasive.
- What to Tell Your Dentist Before You Have a Tooth Pulled:
- Damaged heart valves
- Congenital heart defect
- Compromised immune system
- Liver diseases
- Joint replacements
- History of bacterial endocarditis
- When to visit the Dentist in Emergency
- infection with high fever with chills
- Nausea or vomiting
- Redness or swelling.
- Excessive discharge
- Cough or shortness of breath
- chest pain, or severe nausea or vomiting